Understanding the Income Statement
An income statement, also known as a profit and loss statement, is a financial statement that portrays a company’s profitability over a specific period. The income statement summarizes the company’s revenues and expenses and calculates its net income (profit or loss) over the period. This article will discuss the format of an income statement, its components, and how to create one.
The format of an Income Statement
The two main formats of an income statement are the single-step and the multi-step income statements. The single-step income statement is more straightforward, and it groups all of the revenues and expenses together. In contrast, the multi-step income statement separately lists a company’s revenues and expenses into different categories.
Single-Step Income Statement
The single-step income statement’s format is straightforward and only requires a single calculation to determine a company’s net income or net loss.
Multi-Step Income Statement
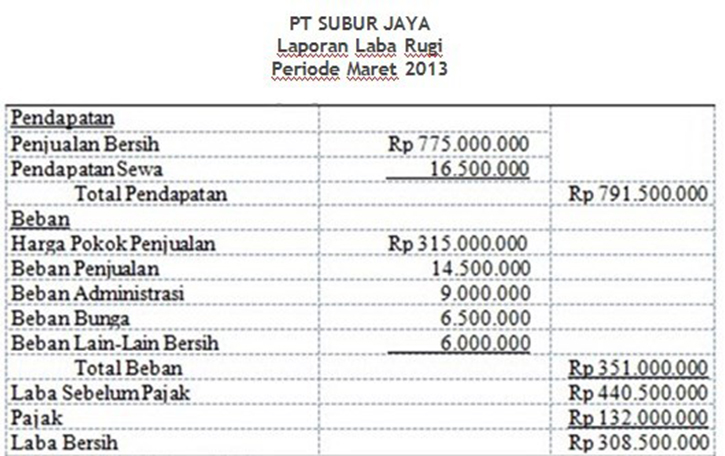
The multi-step income statement separates a company’s revenues and expenses into specific categories. It provides a more detailed look at a company’s profitability and is traditionally used by larger companies.
The Components of an Income Statement
An income statement includes several components that contribute to a company’s net income or net loss:
1. Revenue
Revenue is the income generated by a company’s primary business activities. These activities are typically the sale of goods or services. Revenue is reported at the top of the income statement, and the total revenue for the period is reported as gross revenue.
2. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
Cost of Goods Sold represents the expenses incurred in producing and selling the goods sold by a company. This includes the cost of the materials, labor, and other expenses directly associated with the production of goods. The cost of goods sold is deducted from the company’s gross revenue to determine the gross profit.
3. Gross Profit
Gross profit is the profit margin made by a company before deducting its operating expenses for the period. This is calculated by subtracting the cost of goods sold from the company’s gross revenue.
4. Operating Expenses
Operating expenses are the expenses incurred by a company in carrying out its business activities. This includes rent, utilities, salaries, taxes, and other general expenses. Operating expenses are deducted from the gross profit to determine the operating income.
5. Operating Income
Operating income is the profit earned by a company from its primary business activities. This is calculated by subtracting the company’s operating expenses from its gross profit.
6. Non-Operating Income and Expenses
Non-operating income and expenses are the events or transactions outside of a company’s primary business activities. This includes investments, loans, interest income, and interest expenses. Non-operating income is added, and non-operating expenses are deducted from the operating income to arrive at the pre-tax income.
7. Pre-Tax Income
Pre-tax income is the company’s income or loss before taxes are deducted. This is calculated by adding non-operating income and expenses to the operating income.
8. Taxes
Taxes are the expenses incurred by a company that is based on its taxable income for a given period. Taxes are determined based on the tax laws in the company’s jurisdiction.
9. Net Income or Net Loss
The final component of an income statement is the net income or net loss. This is calculated by subtracting taxes from the pre-tax income.
Creating an Income Statement
The process of creating an income statement can be straightforward or complex, depending on the size and complexity of the company. Here are general steps to follow when creating an income statement:
1. Gather Financial Data
Collect all the financial data needed for the income statement. This includes revenue, cost of goods sold, operating expenses, non-operating income and expenses, and taxes.
2. Determine the Income Statement Format
Determine the format of the income statement to be used. This can either be single-step or multi-step income statement
3. Calculate Gross Profit
Calculate the company’s gross profit by subtracting its cost of goods sold from its total revenue.
4. Calculate Operating Income
Calculate the company’s operating income by subtracting its operating expenses from its gross profit.
5. Add or Subtract Non-Operating Income and Expenses
Add or subtract non-operating income and expenses from the operating income to arrive at pre-tax income.
6. Deduct Taxes
Deduct taxes from the pre-tax income to arrive at the net income or net loss.
FAQs about Income Statement
1. What is the importance of an income statement?
An income statement is essential to the overall financial health of a company. It provides information on the company’s profitability, growth, and financial stability. An income statement aids in decision-making by providing insight into a company’s performance over a given period.
2. How often should an income statement be prepared?
An income statement should be prepared at the end of each accounting period, usually quarterly or annually.